Appendix B: Integration Ecosystem
How ChatML Interacts with LangChain, LlamaIndex, and Other Frameworks
This appendix describes the integration landscape of ChatML — explaining how its structured message format interoperates with modern LLM frameworks such as LangChain, LlamaIndex, and other orchestration libraries.
It outlines adapter patterns, conversion utilities, and best practices that enable seamless use of ChatML inside high-level agent frameworks, retrieval pipelines, and multi-tool systems.
Examples from the Project Support Bot show how ChatML acts as the unifying contract between user intent, model reasoning, and tool execution.
ChatML, LLMs, Prompt Engineering, LangChain, LlamaIndex, Structured Prompting, AI Development, Conversational AI, OpenAI, GPT, Claude, FastAPI, Ollama, Tool Integration, Memory Management
Appendix B: Integration Ecosystem
B.1 Introduction — ChatML as an Interoperability Standard
While ChatML defines how messages are structured, frameworks such as LangChain, LlamaIndex, and Haystack define how those messages are executed.
Together they form a complete stack:
| Layer | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ChatML | Message syntax and roles | <|im_start|>assistant ... <|im_end|> |
| Pipeline Framework | Routing, memory, tool invocation | LangChain / LlamaIndex |
| Model Backend | Inference engine | OpenAI API, Ollama, vLLM |
| Storage & Memory | Context persistence | Qdrant / Pinecone / FAISS |
In this architecture, ChatML serves as the lingua franca that keeps message formats consistent and reproducible across frameworks.
B.2 Integrating ChatML with LangChain
LangChain’s Core Concepts
LangChain models a conversation as a chain of components:
PromptTemplateLLMChainToolandAgentExecutorMemory
ChatML complements these by providing an explicit markup schema for message serialization.
Adapter: ChatML <-> LangChain Message
LangChain uses the class BaseMessage (with subclasses HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage, FunctionMessage).
A simple adapter translates ChatML blocks into these message objects:
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage,
FunctionMessage
def chatml_to_langchain(messages):
mapping = {
"system": SystemMessage,
"user": HumanMessage,
"assistant": AIMessage,
"tool": FunctionMessage
}
return [mapping[m["role"]](content=m["content"]) for m in messages]Example Integration in Project Support Bot
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
lc_messages = chatml_to_langchain(chatml_messages)
chain = LLMChain(llm=ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo"))
response = chain.run(input=lc_messages)This adapter ensures LangChain’s LLMChain can directly interpret ChatML formatted conversations.
B.3 LangChain Tool Execution Layer
LangChain’s Tool objects align naturally with ChatML’s tool role.
Tool Definition
from langchain.tools import tool
@tool("fetch_jira_tickets")
def fetch_jira_tickets(sprint: str):
# Actual logic omitted for brevity
return {"sprint": sprint, "open": 3, "closed": 15}ChatML Representation
<|im_start|>tool
fetch_jira_tickets(sprint="Sprint 5")
<|im_end|>When the assistant emits this message, the LangChain AgentExecutor interprets it and triggers the corresponding Tool.
This preserves semantic clarity and audit traceability.
B.4 Memory and State Bridging via LangChain
ChatML’s memory role aligns with LangChain’s ConversationBufferMemory and VectorStoreRetrieverMemory.
Pattern
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True)
for m in messages:
memory.chat_memory.add_message(chatml_to_langchain([m])[0])This bridges ChatML transcripts with LangChain’s persistent memory stack, enabling replay and contextual injection exactly as described in Chapter 9.
B.5 Integrating ChatML with LlamaIndex (Indexing & Retrieval)
Why LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex (formerly GPT Index) provides advanced retrieval and context augmentation capabilities.
It can consume ChatML transcripts as structured documents or as conversation nodes.
Adapter: ChatML → LlamaIndex Nodes
from llama_index.core import Document
def chatml_to_llamaindex(messages):
return [
Document(
text=m["content"],
metadata={"role": m["role"], "chatml_role": m["role"]}
)
for m in messages
]These Document objects can then be embedded and stored in a vector index (Qdrant, Pinecone, etc.).
Example Use in Project Support Bot
docs = chatml_to_llamaindex(chatml_history)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(docs)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query("Show velocity trend for last 3 sprints.")Here ChatML provides consistent conversation segmentation — each Document is a structured turn with role context.
B.6 Function Calling and Tool Binding in LlamaIndex
LlamaIndex supports FunctionCallingLLM similar to LangChain’s tools.
Example Adapter
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4-turbo", mode="function_calling")
tool_message = {
"role": "tool",
"name": "fetch_jira_tickets",
"arguments": {"sprint": "5"}
}
llm_response = llm.predict(messages=[tool_message])This preserves the ChatML tool schema while leveraging LlamaIndex’s managed execution graph.
B.7 Other Framework Integrations
| Framework | Integration Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Haystack | Wrap ChatML messages in Document objects for retrieval |
Compatible with Elastic or FAISS |
| DSPy | Use ChatML as serialization format for structured prompts | Declarative prompt building |
| FastAPI / Ollama | Pass ChatML encoded prompts to custom streaming LLM endpoints | Deterministic input validation |
| LangGraph / CrewAI | Map roles (planner, executor, critic) to ChatML role fields |
Multi-agent coordination |
| Qdrant | Use ChatML transcripts as embedding source for memory recall | Reproducible vector context |
B.8 Conversion Utilities Library
To standardize integration across frameworks, you can implement a shared chatml_utils.py module.
def encode_to_chatml(messages): ...
def decode_from_chatml(text): ...
def chatml_to_langchain(messages): ...
def chatml_to_llamaindex(messages): ...
def log_chatml_event(role, content, timestamp): ...This common library becomes the adapter layer between frameworks — ensuring every component speaks ChatML.
B.9 Streaming and Telemetry Interoperability
When using streaming APIs (e.g., OpenAI’s ChatCompletion.stream or Ollama’s /api/generate), ChatML’s <|im_sep|> and metadata markers support real-time telemetry.
Example
for chunk in llm.stream(chatml_prompt):
if "<|im_sep|>" in chunk:
log_event("stream_split", chunk)This feeds observability dashboards described in Chapter 10, allowing cross-framework latency and token monitoring.
B.10 Versioning and Schema Governance
To maintain compatibility across LangChain or LlamaIndex updates, each ChatML adapter should specify a schema version.
{
"chatml_version": "1.0.0",
"framework_adapter": "langchain@0.3",
"validated": true
}This metadata can be attached as a <|metadata|> block or stored in your project’s configuration registry.
B.11 Example Ecosystem Flow — Project Support Bot
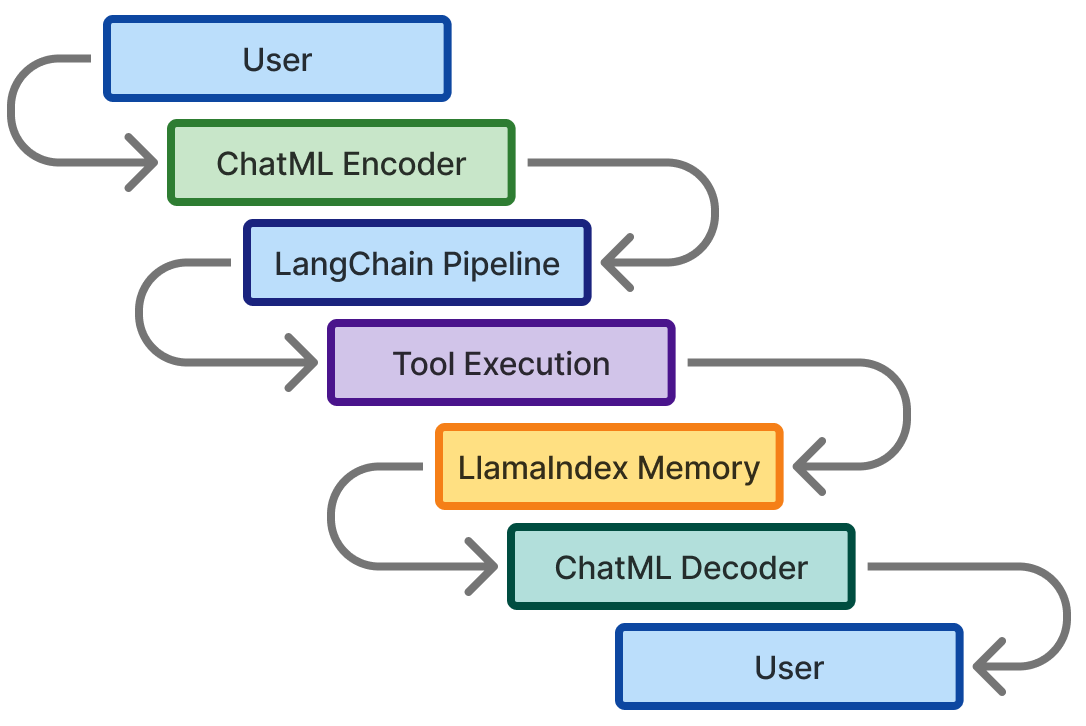
| Stage | Framework | ChatML Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Input Encoding | Custom Encoder | Generates <|im_start|> blocks |
| Prompt Routing | LangChain LLMChain | Converts ChatML → LangChain Messages |
| Tool Execution | LangChain Tools | Reads tool role from ChatML |
| Memory Recall | LlamaIndex Retriever | Stores ChatML messages as Documents |
| Output Formatting | ChatML Decoder | Returns reproducible assistant responses |
This flow illustrates how ChatML remains the structural thread that binds diverse framework layers into a coherent conversation system.
B.12 Extending the Ecosystem
Future integrations may include:
- OpenDevin / AutoGPT for autonomous agent planning
- Semantic Kernel for .NET ecosystem compatibility
- Transformers Agent API for direct PyTorch inference
- LangServe for serving ChatML chains over HTTP
Each can consume ChatML messages as input schemas, reinforcing cross-framework reproducibility.
B.13 Best Practices for Integration
| Guideline | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Source of Truth | Maintain ChatML as canonical format; generate framework objects on demand. |
| Adapters Not Forks | Avoid framework-specific ChatML variations; use conversion functions. |
| Validation Before Execution | Run schema and role checks before passing to framework. |
| Consistent Logging | Emit identical structured logs across frameworks. |
| Version Pinning | Lock framework versions to preserve prompt determinism. |
B.14 Closing Summary
ChatML operates as a meta-protocol above modern LLM frameworks. By offering structured roles, semantic markers, and context replay, it unifies LangChain’s tool logic and LlamaIndex’s memory management under a single communication grammar.
| Aspect | ChatML Contribution | Framework Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Prompt Structure | Deterministic role markup | Stable prompt engineering |
| Memory Replay | Vector context serialization | Improved recall accuracy |
| Tool Invocation | Explicit tool role |
Safe, auditable execution |
| Observability | Metadata and markers | Cross-stack telemetry |
| Portability | Language-agnostic schema | Plug-and-play framework support |
In essence, ChatML acts as the semantic glue of the LLM integration ecosystem — enabling developers to compose, trace, and reproduce intelligent systems with confidence and clarity.